Book an Appointment
Pigmentation
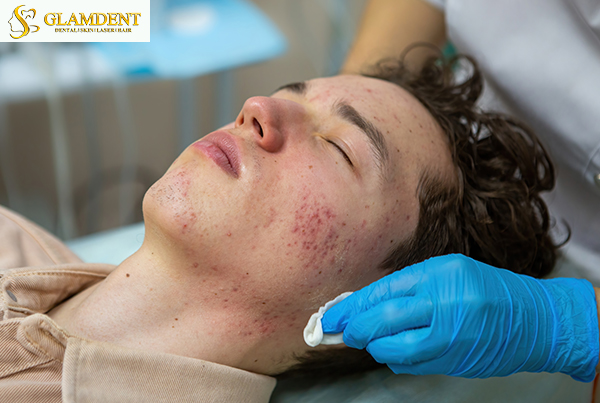
Pigmentation
Pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin, which is determined by the presence of a pigment called melanin. Melanin is produced by melanocytes, cells found in the epidermis (the outer layer of the skin). Skin pigmentation can vary among individuals due to factors such as genetics, sun exposure, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions. Common pigmentation concerns include hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation.
Here are some common types of pigmentation issues and potential treatments:
-
Hyperpigmentation:
- Sunspots or Age Spots: These are dark spots that develop on sun-exposed areas of the skin due to prolonged sun exposure.
- Melasma: This is a condition characterized by brown or grayish-brown patches on the face, often associated with hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or birth control use.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Dark spots that result from inflammation or injury to the skin, such as acne or wounds.
Treatments:
- Topical Skin Lightening Agents: Ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, vitamin C, and alpha arbutin can help lighten dark spots.
- Chemical Peels: Peels with ingredients like glycolic acid or salicylic acid can promote exfoliation and reduce hyperpigmentation.
- Laser Therapy: Various laser treatments, including intense pulsed light (IPL) or fractional laser, can target and break down pigmented cells.
- Microdermabrasion: This exfoliation technique can improve skin texture and reduce pigmentation.
-
Hypopigmentation:
- Vitiligo: This autoimmune condition causes the loss of pigmentation in certain areas of the skin, resulting in white patches.
- Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation: Lightening of the skin after inflammation or injury, such as burns or certain skin conditions.
Treatments:
- Topical Steroids: In some cases of post-inflammatory hypopigmentation, topical steroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and promote repigmentation.
- Phototherapy: Narrowband UVB phototherapy may be used to stimulate melanocyte activity and repigmentation.
- Micropigmentation (Tattooing): In cases of vitiligo, micropigmentation or tattooing may be used to add pigment to the affected areas.
Category: Skin
Get In Touch
Tags
- Glamdent Sector 70 Gurugram
- Glamdent clinic
- dr harshita
- Best cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best cosmetology clinic in Gurugram Sector 70
- Cosmetology doctor in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best onco dental surgeon in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best dentist in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram Sector 70
- Laser Hair Reduction in Gurugram Sector 70
- Mole Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Tag Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Wart Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best clinic for Beard shaping in Gurugram Sector 70
- Advance Hydra facial in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best Photo facial treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- BB glow treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Anti aging treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Skin brightening treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- PRP therapy for hair in Gurugram Sector 70
- Prp therapy for skin in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best clinic for Vampire Facial in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best clinic for Mesotherapy in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best Microblading treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Treatment for Lip tint in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best treatment for Carbon laser in Gurugram Sector 70
- Chemical peels treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Tattoo removal clinic in Gurugram Sector 70
- Treatment for Teeth cleaning in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best treatment for Teeth whitening in Gurugram Sector 70
- Root canal treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- RCT treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Tooth Extraction in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best treatment for cosmetic Filling in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best dental Implant clinic in Gurugram Sector 70
- Tobacco cessation clinic in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best cosmetology clinic in Gurugram Sector 71
- Cosmetology doctor in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best onco dental surgeon in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best dentist in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram Sector 71
- Laser Hair Reduction in Gurugram Sector 71
- Mole Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Tag Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Wart Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best clinic for Beard shaping in Gurugram Sector 71
- Advance Hydra facial in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best Photo facial treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- BB glow treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Anti aging treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Skin brightening treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- PRP therapy for hair in Gurugram Sector 71
- Prp therapy for skin in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best clinic for Vampire Facial in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best clinic for Mesotherapy in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best Microblading treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Treatment for Lip tint in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best treatment for Carbon laser in Gurugram Sector 71
- Chemical peels treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Tattoo removal clinic in Gurugram Sector 71
- Treatment for Teeth cleaning in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best treatment for Teeth whitening in Gurugram Sector 71
- Root canal treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- RCT treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Tooth Extraction in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best treatment for cosmetic Filling in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best dental Implant clinic in Gurugram Sector 71
- Tobacco cessation clinic in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best cosmetology clinic in Gurugram Sector 69
- Cosmetology doctor in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best onco dental surgeon in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best dentist in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram Sector 69
- Laser Hair Reduction in Gurugram Sector 69
- Mole Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Tag Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Wart Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best clinic for Beard shaping in Gurugram Sector 69
- Advance Hydra facial in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best Photo facial treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- BB glow treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Anti aging treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Skin brightening treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- PRP therapy for hair in Gurugram Sector 69
- Prp therapy for skin in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best clinic for Vampire Facial in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best clinic for Mesotherapy in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best Microblading treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Treatment for Lip tint in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best treatment for Carbon laser in Gurugram Sector 69
- Chemical peels treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Tattoo removal clinic in Gurugram Sector 69
- Treatment for Teeth cleaning in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best treatment for Teeth whitening in Gurugram Sector 69
- Root canal treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- RCT treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Tooth Extraction in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best treatment for cosmetic Filling in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best dental Implant clinic in Gurugram Sector 69
- Tobacco cessation clinic in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best cosmetology clinic in Gurugram Sector 73
- Cosmetology doctor in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best onco dental surgeon in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best dentist in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram Sector 73
- Laser Hair Reduction in Gurugram Sector 73
- Mole Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Tag Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Wart Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best clinic for Beard shaping in Gurugram Sector 73
- Advance Hydra facial in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best Photo facial treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- BB glow treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Anti aging treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Skin brightening treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- PRP therapy for hair in Gurugram Sector 73
- Prp therapy for skin in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best clinic for Vampire Facial in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best clinic for Mesotherapy in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best Microblading treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Treatment for Lip tint in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best treatment for Carbon laser in Gurugram Sector 73
- Chemical peels treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Tattoo removal clinic in Gurugram Sector 73
- Treatment for Teeth cleaning in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best treatment for Teeth whitening in Gurugram Sector 73
- Root canal treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- RCT treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Tooth Extraction in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best treatment for cosmetic Filling in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best dental Implant clinic in Gurugram Sector 73
- Tobacco cessation clinic in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best cosmetology clinic in Gurugram Sector 75
- Cosmetology doctor in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best onco dental surgeon in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best dentist in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram Sector 75
- Laser Hair Reduction in Gurugram Sector 75
- Mole Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Tag Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Wart Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best clinic for Beard shaping in Gurugram Sector 75
- Advance Hydra facial in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best Photo facial treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- BB glow treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Anti aging treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Skin brightening treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- PRP therapy for hair in Gurugram Sector 75
- Prp therapy for skin in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best clinic for Vampire Facial in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best clinic for Mesotherapy in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best Microblading treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Treatment for Lip tint in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best treatment for Carbon laser in Gurugram Sector 75
- Chemical peels treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Tattoo removal clinic in Gurugram Sector 75
- Treatment for Teeth cleaning in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best treatment for Teeth whitening in Gurugram Sector 75
- Root canal treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- RCT treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Tooth Extraction in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best treatment for cosmetic Filling in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best dental Implant clinic in Gurugram Sector 75
- Tobacco cessation clinic in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best cosmetology clinic in Gurugram Sector 76
- Cosmetology doctor in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best onco dental surgeon in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best dentist in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram Sector 76
- Laser Hair Reduction in Gurugram Sector 76
- Mole Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Tag Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Wart Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best clinic for Beard shaping in Gurugram Sector 76
- Advance Hydra facial in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best Photo facial treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- BB glow treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Anti aging treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Skin brightening treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- PRP therapy for hair in Gurugram Sector 76
- Prp therapy for skin in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best clinic for Vampire Facial in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best clinic for Mesotherapy in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best Microblading treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Treatment for Lip tint in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best treatment for Carbon laser in Gurugram Sector 76
- Chemical peels treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Tattoo removal clinic in Gurugram Sector 76
- Treatment for Teeth cleaning in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best treatment for Teeth whitening in Gurugram Sector 76
- Root canal treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- RCT treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Tooth Extraction in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best treatment for cosmetic Filling in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best dental Implant clinic in Gurugram Sector 76
- Tobacco cessation clinic in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best cosmetology clinic in Gurugram Sector 77
- Cosmetology doctor in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best onco dental surgeon in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best dentist in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram Sector 77
- Laser Hair Reduction in Gurugram Sector 77
- Mole Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Tag Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Wart Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best clinic for Beard shaping in Gurugram Sector 77
- Advance Hydra facial in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best Photo facial treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- BB glow treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Anti aging treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Skin brightening treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- PRP therapy for hair in Gurugram Sector 77
- Prp therapy for skin in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best clinic for Vampire Facial in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best clinic for Mesotherapy in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best Microblading treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Treatment for Lip tint in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best treatment for Carbon laser in Gurugram Sector 77
- Chemical peels treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Tattoo removal clinic in Gurugram Sector 77
- Treatment for Teeth cleaning in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best treatment for Teeth whitening in Gurugram Sector 77
- Root canal treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- RCT treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Tooth Extraction in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best treatment for cosmetic Filling in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best dental Implant clinic in Gurugram Sector 77
- Tobacco cessation clinic in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best cosmetology clinic in Gurugram Sector 72
- Cosmetology doctor in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best onco dental surgeon in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best dentist in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram Sector 72
- Laser Hair Reduction in Gurugram Sector 72
- Mole Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Tag Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Wart Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best clinic for Beard shaping in Gurugram Sector 72
- Advance Hydra facial in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best Photo facial treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- BB glow treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Anti aging treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Skin brightening treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- PRP therapy for hair in Gurugram Sector 72
- Prp therapy for skin in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best clinic for Vampire Facial in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best clinic for Mesotherapy in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best Microblading treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Treatment for Lip tint in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best treatment for Carbon laser in Gurugram Sector 72
- Chemical peels treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Tattoo removal clinic in Gurugram Sector 72
- Treatment for Teeth cleaning in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best treatment for Teeth whitening in Gurugram Sector 72
- Root canal treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- RCT treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Tooth Extraction in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best treatment for cosmetic Filling in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best dental Implant clinic in Gurugram Sector 72
- Tobacco cessation clinic in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best cosmetology clinic in Gurugram Sector 49
- Cosmetology doctor in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best onco dental surgeon in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best dentist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram Sector 49
- Laser Hair Reduction in Gurugram Sector 49
- Mole Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Tag Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Wart Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best clinic for Beard shaping in Gurugram Sector 49
- Advance Hydra facial in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Photo facial treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- BB glow treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Anti aging treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Skin brightening treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- PRP therapy for hair in Gurugram Sector 49
- Prp therapy for skin in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best clinic for Vampire Facial in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best clinic for Mesotherapy in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Microblading treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Treatment for Lip tint in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best treatment for Carbon laser in Gurugram Sector 49
- Chemical peels treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Tattoo removal clinic in Gurugram Sector 49
- Treatment for Teeth cleaning in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best treatment for Teeth whitening in Gurugram Sector 49
- Root canal treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- RCT treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Tooth Extraction in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best treatment for cosmetic Filling in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best dental Implant clinic in Gurugram Sector 49
- Tobacco cessation clinic in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best cosmetology clinic in Gurugram Sector 47
- Cosmetology doctor in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best onco dental surgeon in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best dentist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram Sector 47
- Laser Hair Reduction in Gurugram Sector 47
- Mole Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Tag Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Wart Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best clinic for Beard shaping in Gurugram Sector 47
- Advance Hydra facial in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Photo facial treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- BB glow treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Anti aging treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Skin brightening treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- PRP therapy for hair in Gurugram Sector 47
- Prp therapy for skin in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best clinic for Vampire Facial in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best clinic for Mesotherapy in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Microblading treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Treatment for Lip tint in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best treatment for Carbon laser in Gurugram Sector 47
- Chemical peels treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Tattoo removal clinic in Gurugram Sector 47
- Treatment for Teeth cleaning in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best treatment for Teeth whitening in Gurugram Sector 47
- Root canal treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- RCT treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Tooth Extraction in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best treatment for cosmetic Filling in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best dental Implant clinic in Gurugram Sector 47
- Tobacco cessation clinic in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best cosmetology clinic in Gurugram Sector 48
- Cosmetology doctor in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best onco dental surgeon in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best dentist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram Sector 48
- Laser Hair Reduction in Gurugram Sector 48
- Mole Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Tag Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Wart Removal treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best clinic for Beard shaping in Gurugram Sector 48
- Advance Hydra facial in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Photo facial treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- BB glow treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Anti aging treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Skin brightening treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- PRP therapy for hair in Gurugram Sector 48
- Prp therapy for skin in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best clinic for Vampire Facial in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best clinic for Mesotherapy in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Microblading treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Treatment for Lip tint in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best treatment for Carbon laser in Gurugram Sector 48
- Chemical peels treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Tattoo removal clinic in Gurugram Sector 48
- Treatment for Teeth cleaning in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best treatment for Teeth whitening in Gurugram Sector 48
- Root canal treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- RCT treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Tooth Extraction in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best treatment for cosmetic Filling in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best dental Implant clinic in Gurugram Sector 48
- Tobacco cessation clinic in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best cosmetologist in Gurugram
- Best cosmetology clinic in Gurugram
- Cosmetology doctor in Gurugram
- Best onco dental surgeon in Gurugram
- Best dentist in Gurugram
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram
- Laser Hair Reduction in Gurugram
- Mole Removal treatment in Gurugram
- Tag Removal treatment in Gurugram
- Wart Removal treatment in Gurugram
- Best clinic for Beard shaping in Gurugram
- Advance Hydra facial in Gurugram
- Best Photo facial treatment in Gurugram
- BB glow treatment in Gurugram
- Anti aging treatment in Gurugram
- Skin brightening treatment in Gurugram
- PRP therapy for hair in Gurugram
- Prp therapy for skin in Gurugram
- Best clinic for Vampire Facial in Gurugram
- Best clinic for Mesotherapy in Gurugram
- Best Microblading treatment in Gurugram
- Treatment for Lip tint in Gurugram
- Best treatment for Carbon laser in Gurugram
- Chemical peels treatment in Gurugram
- Tattoo removal clinic in Gurugram
- Treatment for Teeth cleaning in Gurugram
- Best treatment for Teeth whitening in Gurugram
- Root canal treatment in Gurugram
- RCT treatment in Gurugram
- Tooth Extraction in Gurugram
- Best treatment for cosmetic Filling in Gurugram
- Best dental Implant clinic in Gurugram
- Tobacco cessation clinic in Gurugram
- Best dental clinic in Gurugram
- PRP Treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best Cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 70
- Pigmentation Treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Hydra Facial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best Skin Clinic in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best Hair Treatment Clinic in Gurugram Sector 70
- PRP Treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best Cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 71
- Pigmentation Treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Hydra Facial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best Skin Clinic in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best Hair Treatment Clinic in Gurugram Sector 71
- PRP Treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best Cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 69
- Pigmentation Treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Hydra Facial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best Skin Clinic in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best Hair Treatment Clinic in Gurugram Sector 69
- PRP Treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best Cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 73
- Pigmentation Treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Hydra Facial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best Skin Clinic in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best Hair Treatment Clinic in Gurugram Sector 73
- PRP Treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best Cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 75
- Pigmentation Treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Hydra Facial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best Skin Clinic in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best Hair Treatment Clinic in Gurugram Sector 75
- PRP Treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best Cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 76
- Pigmentation Treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Hydra Facial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best Skin Clinic in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best Hair Treatment Clinic in Gurugram Sector 76
- PRP Treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best Cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 77
- Pigmentation Treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Hydra Facial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best Skin Clinic in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best Hair Treatment Clinic in Gurugram Sector 77
- PRP Treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best Cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 72
- Pigmentation Treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Hydra Facial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best Skin Clinic in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best Hair Treatment Clinic in Gurugram Sector 72
- PRP Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 49
- Pigmentation Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Hydra Facial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Skin Clinic in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Hair Treatment Clinic in Gurugram Sector 49
- PRP Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 47
- Pigmentation Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Hydra Facial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Skin Clinic in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Hair Treatment Clinic in Gurugram Sector 47
- PRP Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Cosmetologist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 48
- Pigmentation Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Hydra Facial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Skin Clinic in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Hair Treatment Clinic in Gurugram Sector 48
- PRP Treatment in Gurugram
- Best Cosmetologist in Gurugram
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram
- Best Dental Implant in Gurugram
- Pigmentation Treatment in Gurugram
- Hydra Facial Treatment in Gurugram
- Best Skin Clinic in Gurugram
- Best Hair Treatment Clinic in Gurugram
- Best Aesthetic Clinic in Gurugram
- Hydrafacial Treatment in Gurugram
- PRP Therapy for skin Treatment in Gurugram
- PRP Therapy for Hair Treatment in Gurugram
- Botox Treatment in Gurugram
- Fillers Treatment for Skin in Gurugram
- Fillers Treatment for Hair in Gurugram
- Chemical Peels Treatment in Gurugram
- Gluta IV Drip Treatment in Gurugram
- Best Aesthetic Clinic in Gurugram Sector 70
- Hydrafacial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- PRP Therapy for skin Treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- PRP Therapy for Hair Treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Botox Treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Fillers Treatment for Skin in Gurugram Sector 70
- Fillers Treatment for Hair in Gurugram Sector 70
- Chemical Peels Treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Gluta IV Drip Treatment in Gurugram Sector 70
- Best Aesthetic Clinic in Gurugram Sector 71
- Hydrafacial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- PRP Therapy for skin Treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- PRP Therapy for Hair Treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Botox Treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Fillers Treatment for Skin in Gurugram Sector 71
- Fillers Treatment for Hair in Gurugram Sector 71
- Chemical Peels Treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Gluta IV Drip Treatment in Gurugram Sector 71
- Best Aesthetic Clinic in Gurugram Sector 72
- Hydrafacial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- PRP Therapy for skin Treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- PRP Therapy for Hair Treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Botox Treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Fillers Treatment for Skin in Gurugram Sector 72
- Fillers Treatment for Hair in Gurugram Sector 72
- Chemical Peels Treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Gluta IV Drip Treatment in Gurugram Sector 72
- Best Aesthetic Clinic in Gurugram Sector 73
- Hydrafacial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- PRP Therapy for skin Treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- PRP Therapy for Hair Treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Botox Treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Fillers Treatment for Skin in Gurugram Sector 73
- Fillers Treatment for Hair in Gurugram Sector 73
- Chemical Peels Treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Gluta IV Drip Treatment in Gurugram Sector 73
- Best Aesthetic Clinic in Gurugram Sector 69
- Hydrafacial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- PRP Therapy for skin Treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- PRP Therapy for Hair Treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Botox Treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Fillers Treatment for Skin in Gurugram Sector 69
- Fillers Treatment for Hair in Gurugram Sector 69
- Chemical Peels Treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Gluta IV Drip Treatment in Gurugram Sector 69
- Best Aesthetic Clinic in Gurugram Sector 75
- Hydrafacial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- PRP Therapy for skin Treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- PRP Therapy for Hair Treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Botox Treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Fillers Treatment for Skin in Gurugram Sector 75
- Fillers Treatment for Hair in Gurugram Sector 75
- Chemical Peels Treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Gluta IV Drip Treatment in Gurugram Sector 75
- Best Aesthetic Clinic in Gurugram Sector 76
- Hydrafacial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- PRP Therapy for skin Treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- PRP Therapy for Hair Treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Botox Treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Fillers Treatment for Skin in Gurugram Sector 76
- Fillers Treatment for Hair in Gurugram Sector 76
- Chemical Peels Treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Gluta IV Drip Treatment in Gurugram Sector 76
- Best Aesthetic Clinic in Gurugram Sector 77
- Hydrafacial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- PRP Therapy for skin Treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- PRP Therapy for Hair Treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Botox Treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Fillers Treatment for Skin in Gurugram Sector 77
- Fillers Treatment for Hair in Gurugram Sector 77
- Chemical Peels Treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Gluta IV Drip Treatment in Gurugram Sector 77
- Best Aesthetic Clinic in Gurugram Sector 49
- Hydrafacial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- PRP Therapy for skin Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- PRP Therapy for Hair Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Botox Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Fillers Treatment for Skin in Gurugram Sector 49
- Fillers Treatment for Hair in Gurugram Sector 49
- Chemical Peels Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Gluta IV Drip Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Aesthetic Clinic in Gurugram Sector 47
- Hydrafacial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- PRP Therapy for skin Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- PRP Therapy for Hair Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Botox Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Fillers Treatment for Skin in Gurugram Sector 47
- Fillers Treatment for Hair in Gurugram Sector 47
- Chemical Peels Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Gluta IV Drip Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Aesthetic Clinic in Gurugram Sector 48
- Hydrafacial Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- PRP Therapy for skin Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- PRP Therapy for Hair Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Botox Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Fillers Treatment for Skin in Gurugram Sector 48
- Fillers Treatment for Hair in Gurugram Sector 48
- Chemical Peels Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Gluta IV Drip Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- show more
- show less








